What is Rotomoulding?
Rotovia has been active in rotomoulding for more then 50 years. Its the process where we brought and will bring many ideas of our customers to life. But what is rotomoulding exactly? On this page you will find an short overview of what rotomoulding is.
Rotomoulding, also known as rotational moulding, is a distinctive manufacturing process utilized in producing hollow plastic products with unparalleled precision and efficiency. This page aims to show you rotomoulding, from its initial steps of material preparation to the finishing and assembling of the final product, while also highlighting its advantages, comparing it with other plastic moulding techniques.
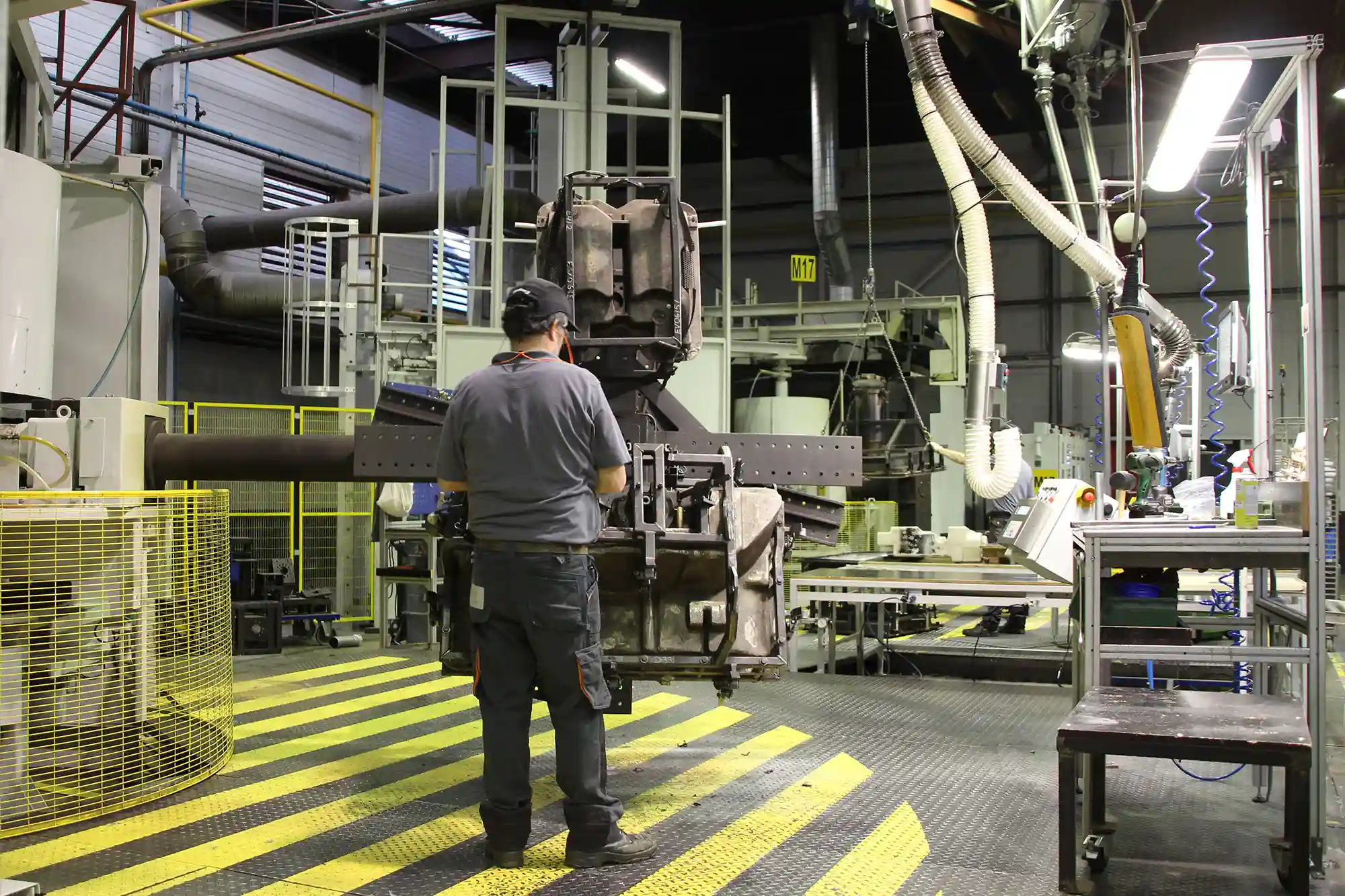

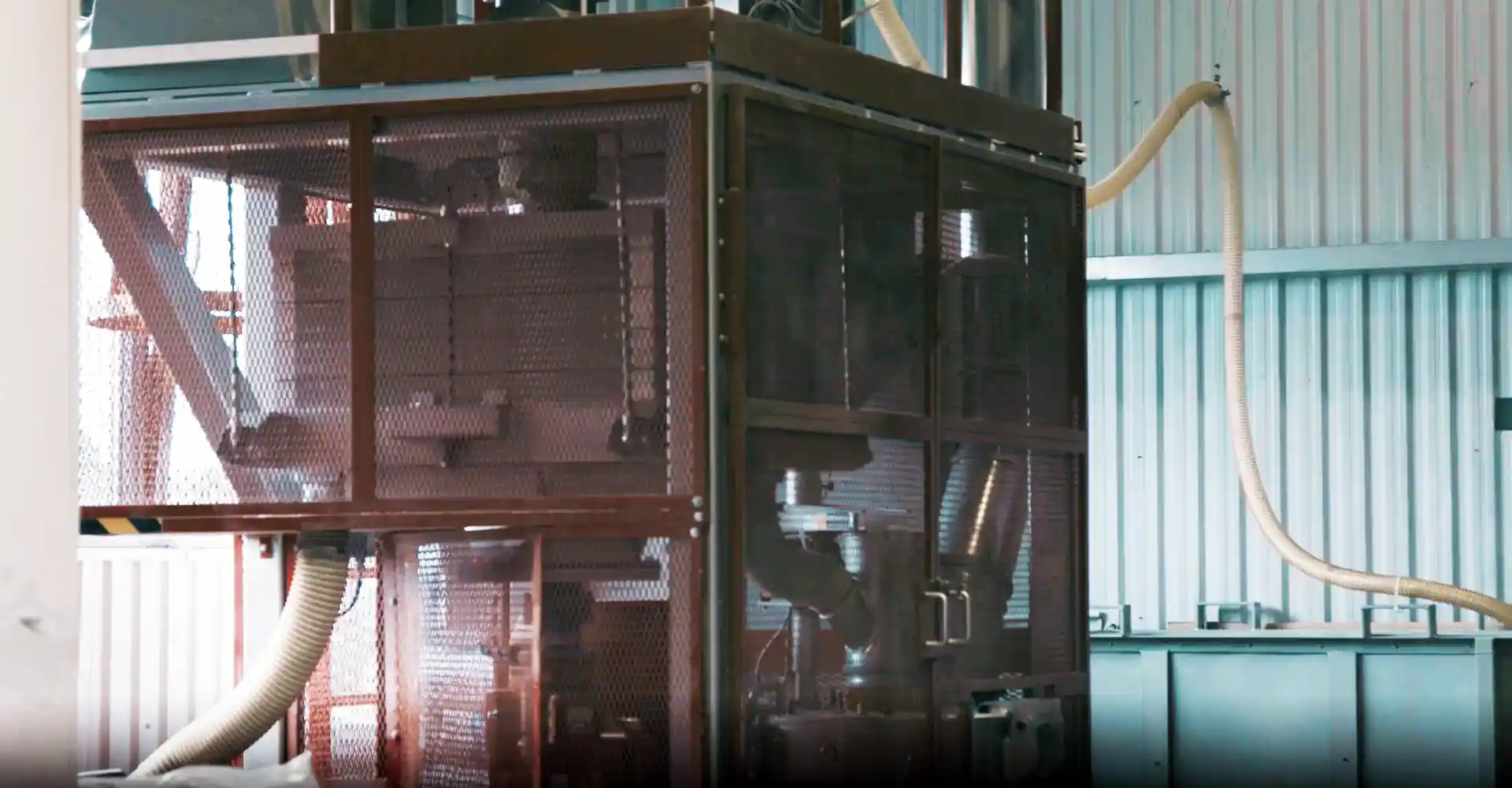
Material Preparation
The first step of the Rotomoulding process is material preparation. The material will be loaded into the mould after the de-moulding process and the mould temperature then is far below the melting temperature of the material. That is why we grind plastic granules into a fine powder. This speeds up the melting of the material, it shortens the cycle time and with this powder we create a very smooth inner surface.
The grinding of the plastic material can be done either with natural or with compounded (colored or blended) granules in a specially designed grinding machine. The granules need to be grinded in powder with a wide range of different lengths and shapes of particles, to improve the material properties at the end of the Rotomoulding process. The different lengths and shapes are required to build a dense material without air inclusions. The ease of flow of the powder is another important property. A good flow ensures that the material runs in all narrow areas of the mould, and prevents pinholes or even larger holes in the product. To monitor the grinding process, several measurements are done on the powder, like measurement of bulk density and dry flow. A sieve test guarantees a good size distribution of the particles – and in the end a good result for the Rotomoulded part.
After the grinding process of natural material, it is possible to dry-blend the material with color or other additives. This is a less costly process, but the distribution of the additive is less fine compared to compounding of additives. For many applications, dry-blending will be a good alternative to compounding.
When the powder is ready, it is pre-weighted in bags containing the right shot weight for the product. The powder can also be fed into the mould directly.
Loading
After the mould has been opened, and the product is released from the mould, the operator starts the loading process of the mould. The operator will clean the mould in areas where necessary and might apply a release agent. When metal inserts are part of the product, the operator will fix the metal inserts to the mould now. Threads or undercuts in a product can be formed using seperable mould parts, these mould parts are installnow. At the last stage the operator closes the mould with the other half of the mould, and fixes the mould with clambs holding the flange of the mould. Then the operator will release the machine to allow the mould to move into the oven, starting the sintering process.

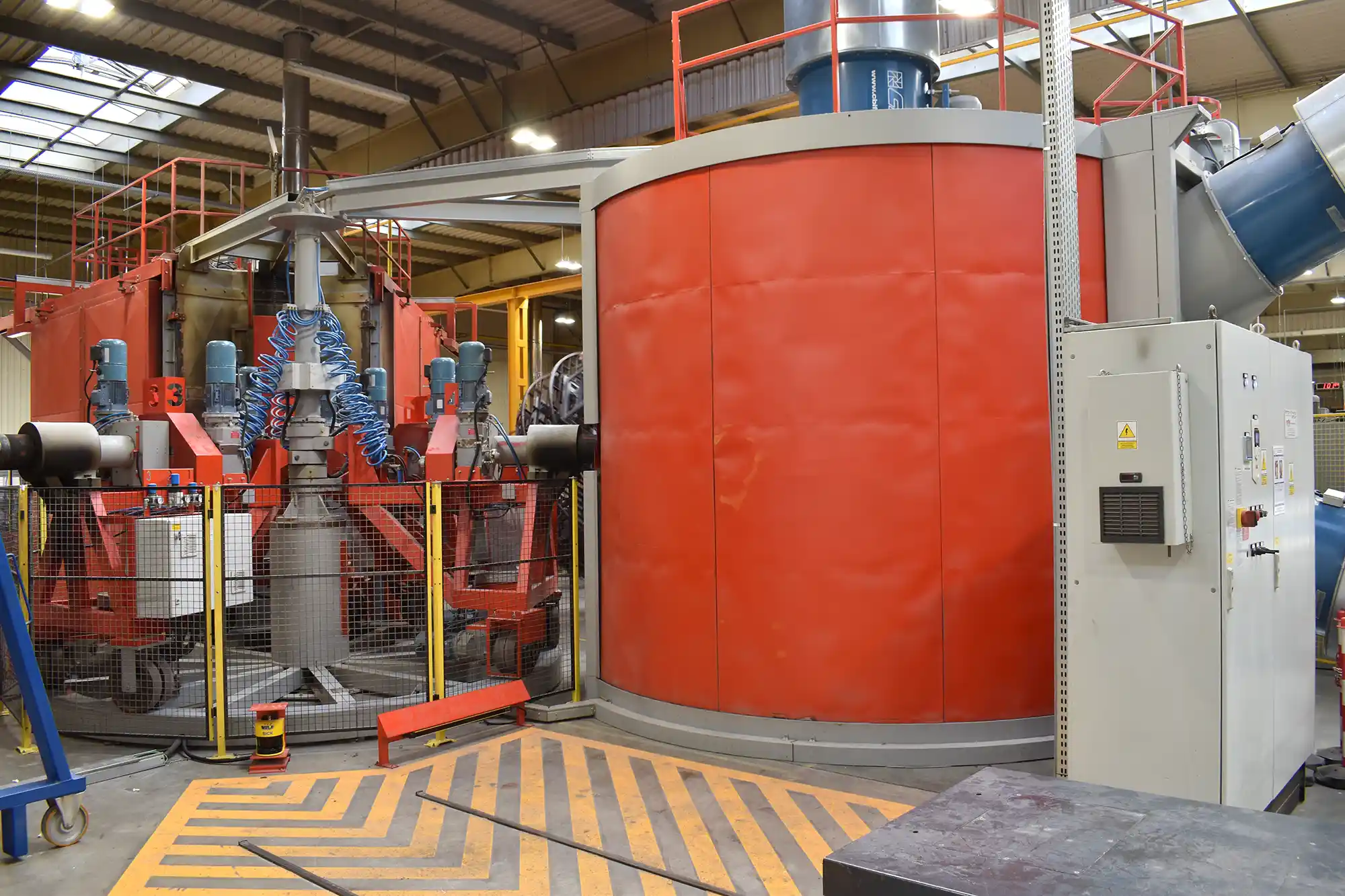
Sintering
The sintering process takes place when moving the mould into a heated oven. Alteratively, a special type of direct-heated mould with build-in electrical heating elements can be used without an oven. The mould is fixed to an arm which rotates the mould in 2 directions, using a primary and secondary axes. This bi-axial movement roll the powder across the surface of the mould. As the mould is heated it reaches the melting point of the plastic – this is when the plastic starts to stick to the mould. Layer by layer the plastic powder reaches every corner of the mould and the wall thickness builds up until the powder has melted completely to the mould. Still the mould will be heated to reach the PIAT (peak internal air temperature), at this point the material is fully fused and pinholes are reduced to a minimum. Now, the plastic is ready to cool down, the mould will be moved out of the oven or in case of direct-heated mould the heating elements are shut off.
Cooling
The cooling process is mostly done using forced air directed at the mould. Sometime this is combined with mist or even spraying water onto the mould. The possible speed of cooling the product depends on the kind of material, the shape of the product and the stage of the material: molten, crystalline phase or solid. The crystallization phase is an important part in the cooling process, determining material properties of the product. The product can also be cooled from the inside by blowing cool air through the inside of the mould into the product and flushing the hot air out through a venting pipe in the mould. When the product is solid and stable enough to de-mould, the mould moves out of the cooling chamber to the de-moulding area.
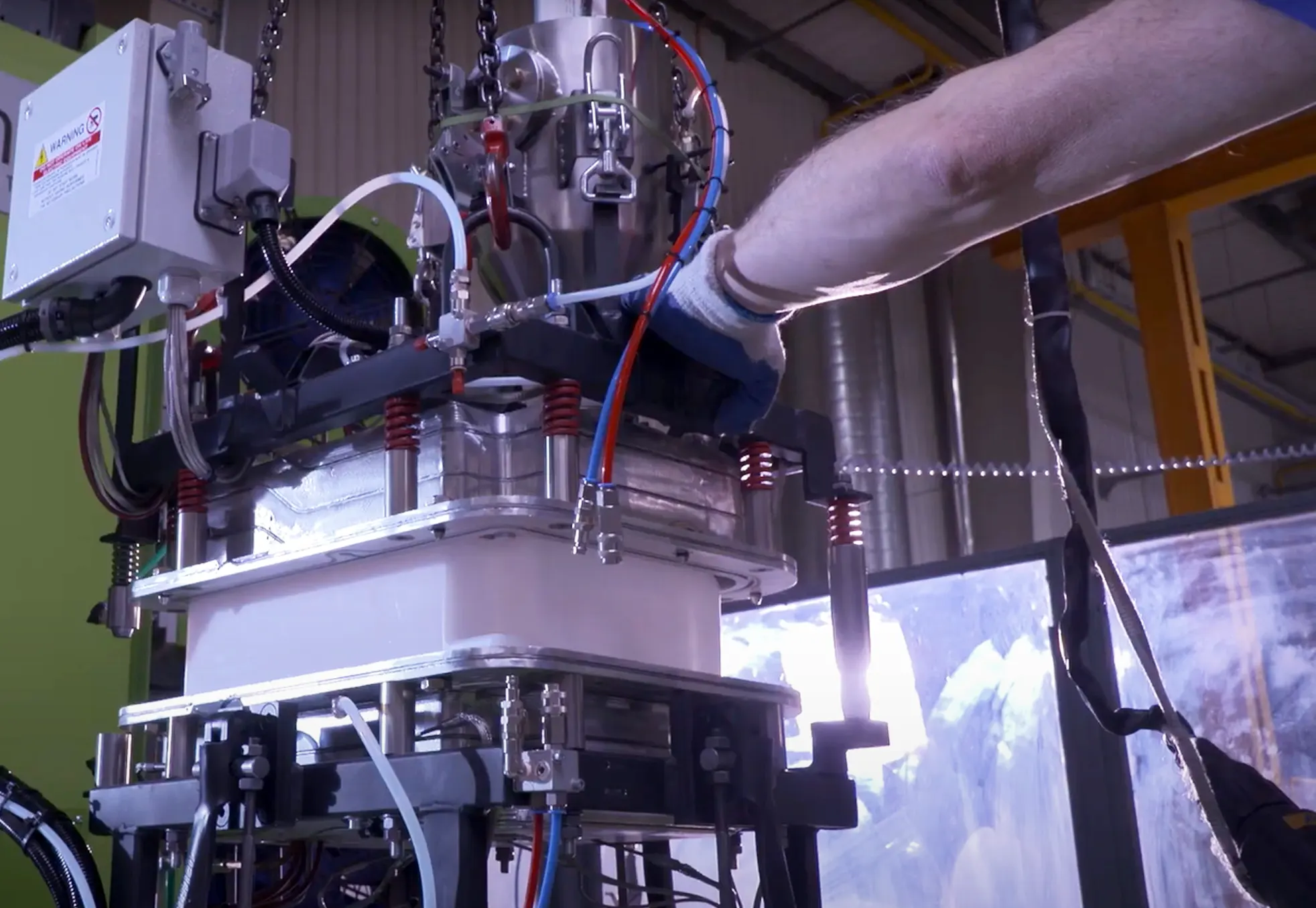


De-moulding
The de-moulding process in rotomoulding is a critical phase where the newly formed plastic product is carefully separated from its mould. This stage requires precise handling to preserve the quality of the product’s surface and dimensions. After the cooling phase, the mould is opened, revealing the solidified plastic item. Operators must ensure that the product is sufficiently cooled and solidified before attempting to remove it to prevent deformation or damage.
The skill in de-moulding lies in the ability to apply the right amount of force and technique to extract the product without leaving marks or causing structural weaknesses. Special tools and techniques may be employed to assist in this process, particularly for complex shapes or designs with intricate details. The success of de-moulding directly influences the final appearance and quality of the rotomoulded product, making it a stage of paramount importance in the manufacturing process.
Finishing & Assembling
After demoulding, the products are moved into a finishing stage. Parting lines are removed. Depending on the product, special cooling provisions may be used to ensure that products are cooled down to room temperature in a controlled way, to minimize the tolerances on dimensions.
If the product requires any sort of machining (drilling or milling), this is performed manually or by means of a finishing robot. With the finishing robot we’ve the possibility to manipulate the product in every direction for optimal flexibility when performing the machining activities. Plastic chips and waste parts from the machining step are collected and recycled. The products are cleaned by means of a vacuum cleaner.
Many products require the assembly of components, or labelling. The components are assembled manually at a finishing department. In some exceptions we use flame polishing to enhance the surface finishing of the products.
In case the products are used for transport or storage of liquids, they will be tested on leak tightness with an automated leak test device. Additional quality checks like wall thickness, weight and a check on the completeness of all the components can be performed. For products with critical applications, we’ve developed fully automated quality checks which are Poke Yoke and have full traceability.
The final finishing step involves the packaging of the products. Although we try to minimise the packaging it can be necessary to put the product in cardboard boxes or plastic bags, depending on the customer demands. For bigger products we often use dedicated transport frames or pallets which are part of a return system.
When the product is packed, finishing will report the product as complete so it’s ready for shipment to our customers.
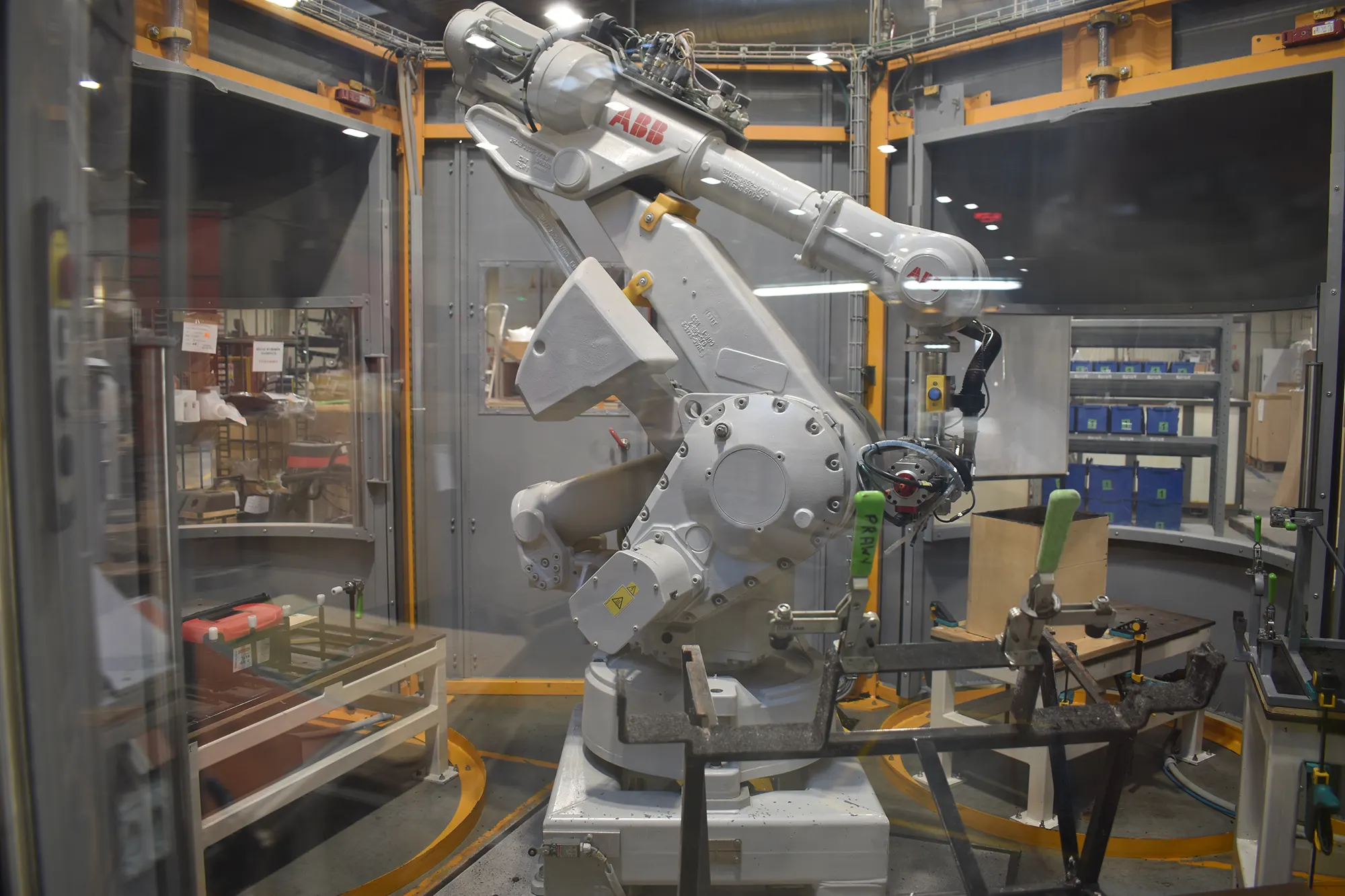
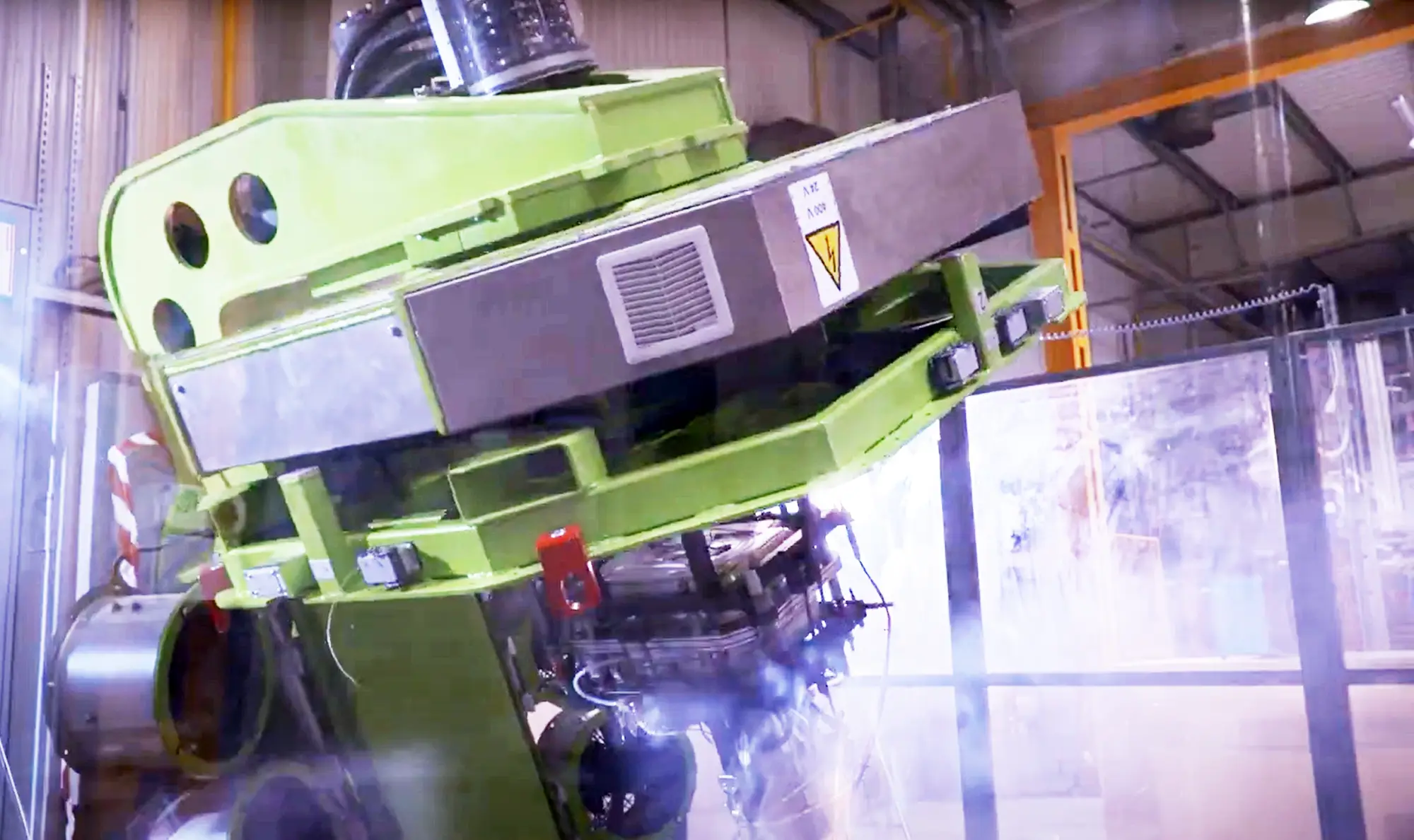


Advantages of Rotomoulding
Advantages of Rotomoulding Rotomoulding has emerged as a key game-changer in the field of plastic manufacture, and its unique set of merits gives it a distinct competitive edge over other moulding processes. The major advantage includes its ability to allow for the production of rather complicated and seamless, hard, and uniform wall thickness products from durable ones. Standout benefits are cost-efficiency, especially for small- to medium-sized production runs; low tooling cost also makes it an excellent choice for custom and low-volume projects compared to the injection or blow moulding process.
Further, rotomoulding allows for materials and colors widest range of selection—thereby accommodating tailor-made products to fit the particular need without steep rise in cost. The process also fares well in the creation of large hollow structures, for example, tanks and containers that are difficult to fabricate using other processes without compromising strength
Another evident advantage is related to the environmental side of rotomoulding. This is due to the fact that the process allows integrating recycled materials into the manufacture and production of only small amounts of waste. The amount of energy used in rotomoulding is normally lower than that of high-pressure techniques, thus becoming another one of the methods preferred by ecologically attentive manufacturers and designers.
Comparing rotomoulding with other plastic moulding techniques
The process of rotomoulding in plastic manufacturing is quite different in nature from other techniques, like injection moulding, or blow moulding etc. In a nutshell, flexibility is one of the great features or advantages of rotomolding in having the ability to produce complex, seamless products of uniform wall thickness, which can never be produced from any other method or way. Where the part produced has a relatively thin wall and there is a need for large quantities, this is best done through injection moulding.
On the other hand, rotomoulding is very good in producing large hollow items with a minimum number of stress points, which enhances durability and longevity of the products. While this is applied to the same creation of hollow objects, this process often lacks the versatility in design and materials use found through rotomoulding processes.
In addition, rotomoulding enjoys added liberty of material with respect to a variety of texture and color variations, along with the ability to easily include inserts or additional features into the design. This, therefore, goes on clearly to explain the niche area of rotomoulding in manufacturing, both for bespoke and quality plastic products, thus proving to be indispensable in cases where precision, product integrity, and design flexibility of the product are indispensable.
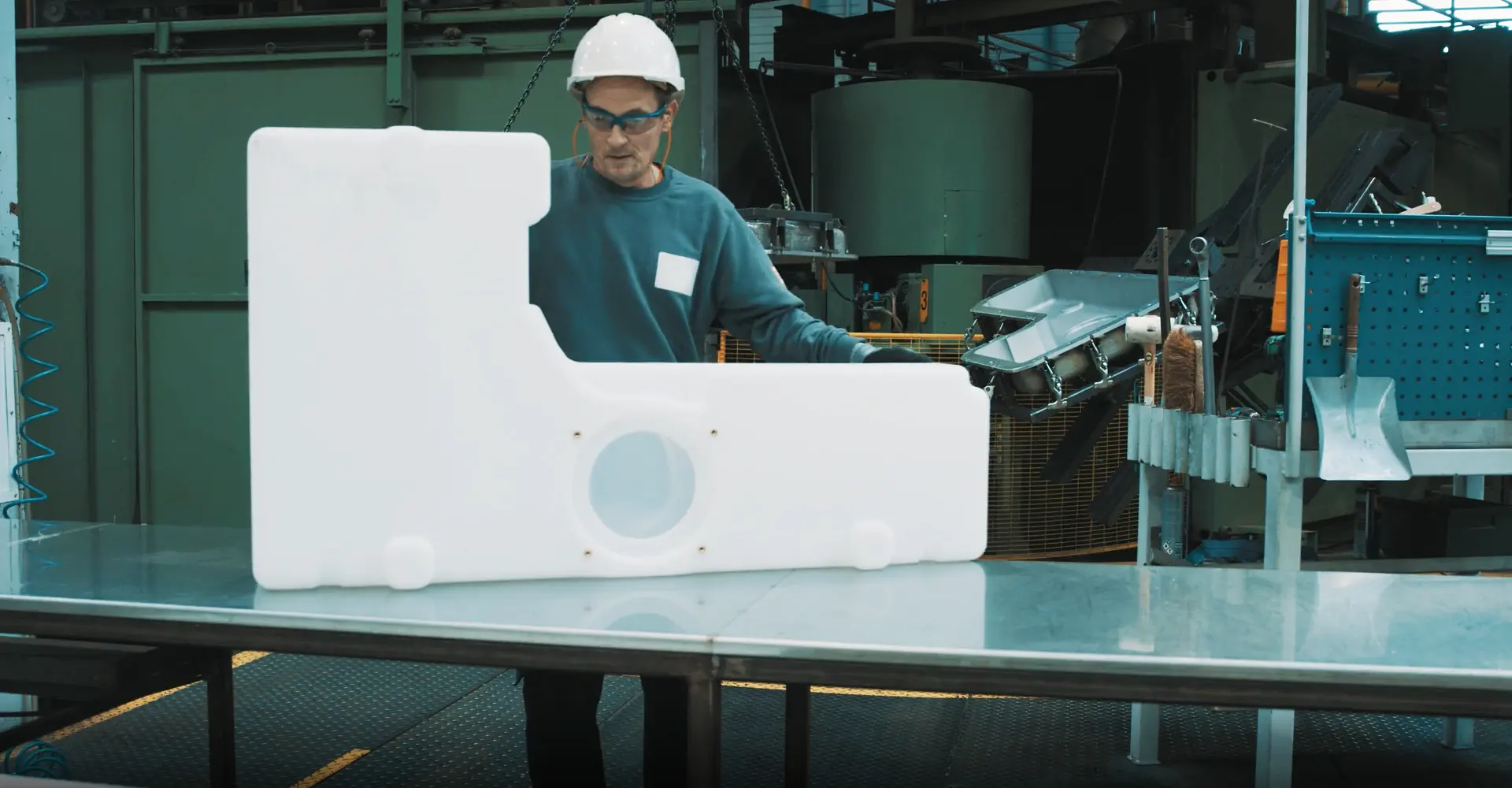
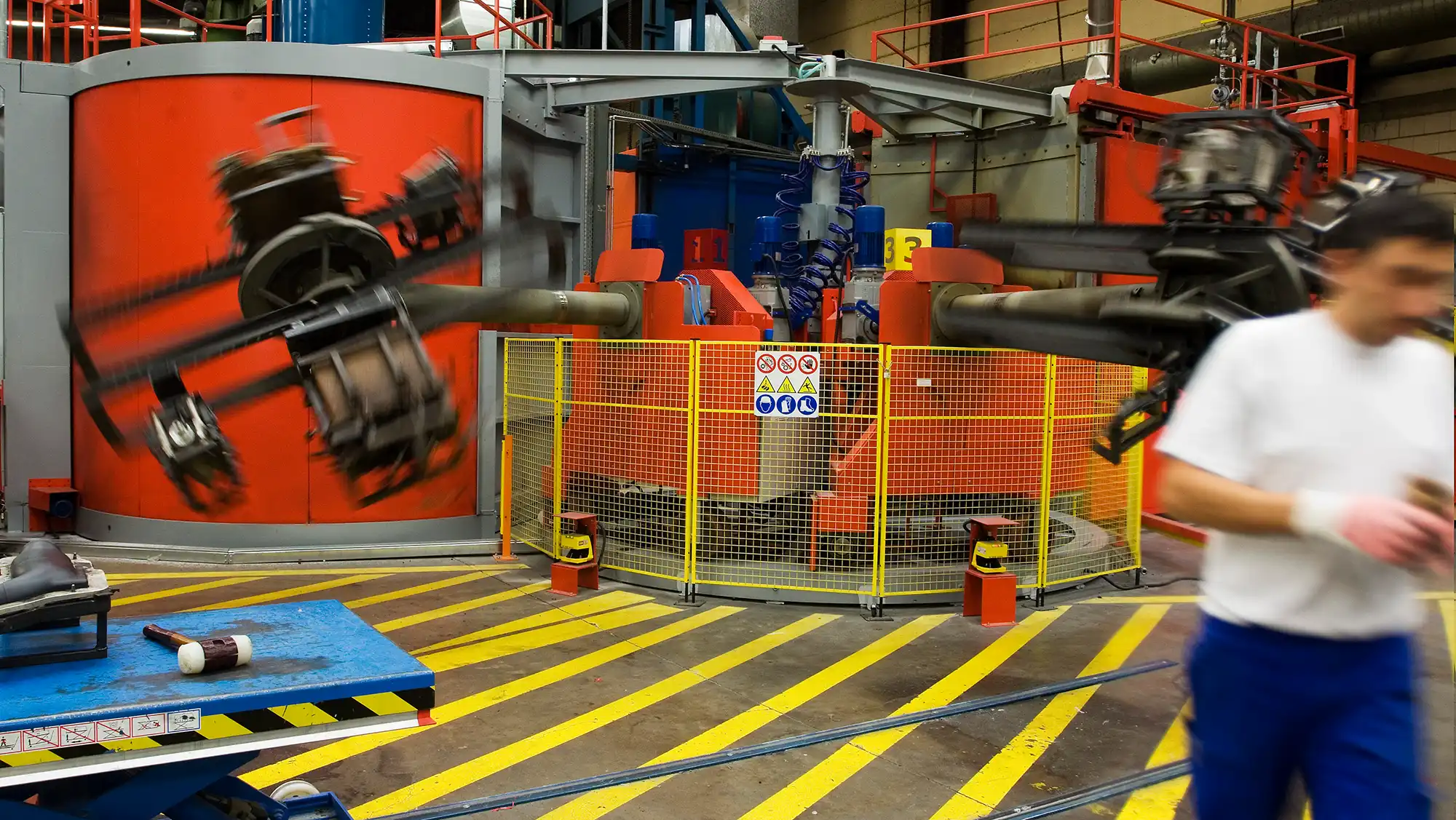


Answering the question what is rotomoulding?
Rotomoulding is a fascinating process that plays a vital role in the plastic manufacturing industry, known for its flexibility, and the high-quality products it produces. As the industry continues to evolve, rotomoulding remains at the forefront of innovation, continually expanding its applications and improving its sustainability. This guide has illuminated the intricacies of rotomoulding, offering insights into its processes, advantages, and comparing it to other techniques, providing a comprehensive answer to the question, “What is rotomoulding?”
your idea
to life. Start now!


