Versatility of polyethylene rotational moulding
Polyethylene for rotational moulding is a lightweight and strong material, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. It is a thermoplastic polymer, which means it can be repeatedly melted and reshaped. Polyethylene is one of the most widely used plastics in the world and is available in a variety of types, including linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), and high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
Polyethylene has excellent chemical resistance. It is resistant to most chemicals, including acids, bases, and organic solvents. We manufacture a wide range of containers for storage, handling and transport of chemicals and tanks for diesel fuel and hydraulic oil. Polyethylene products typically also perform well at lower temperatures: at temperatures as low as -40 °C it still shows its flexibility, resulting in products that are resistant to cold impact.
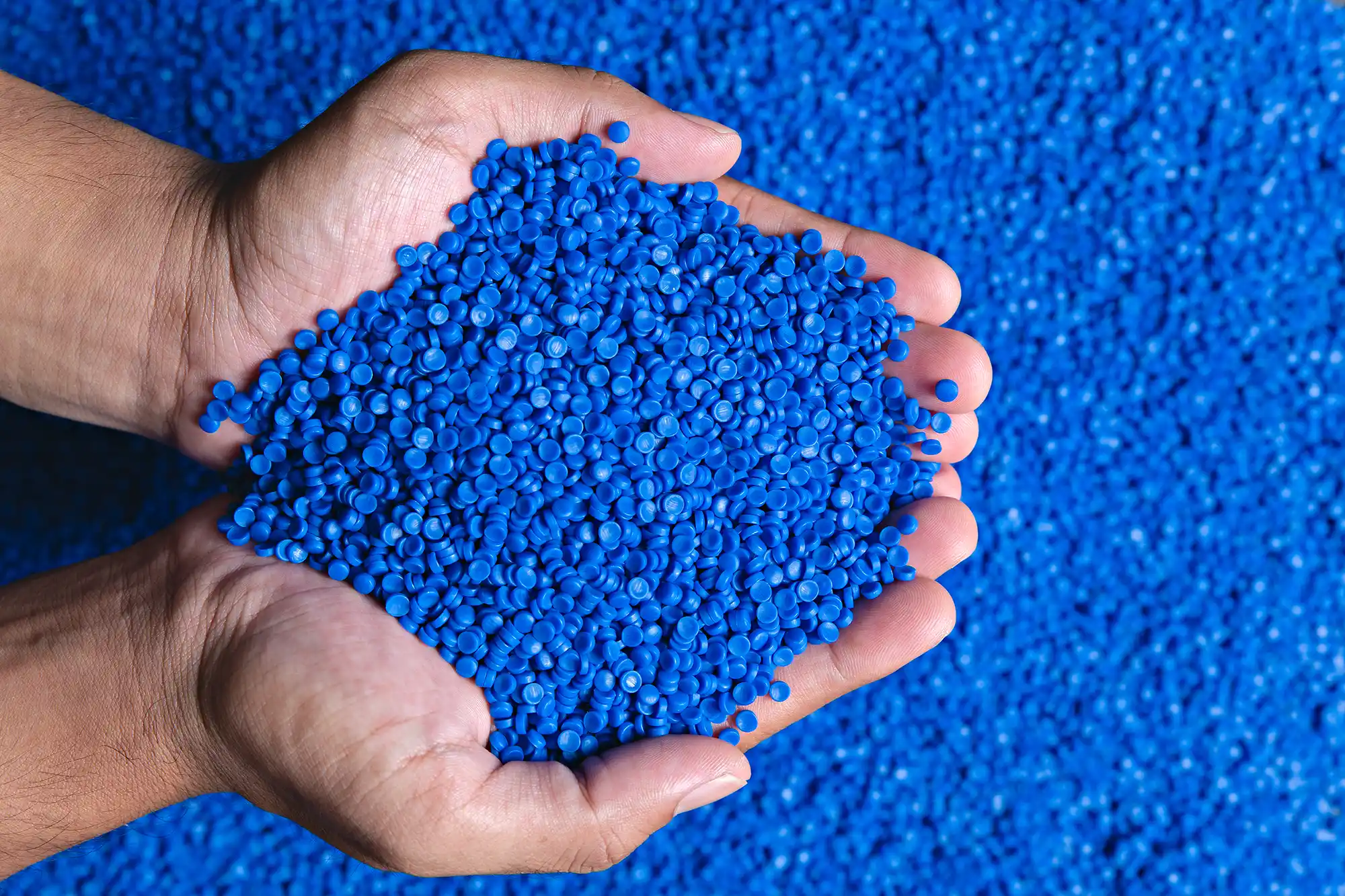


LDPE, LLDPE and HDPE plastic - what's the difference?
LDPE is the most commonly used polyethylene in rotational moulding due to its flexibility, strength and ease of moulding. LLDPE is similar to LDPE, but has higher strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring greater durability. It is used in products such as fuel tanks, technical parts, and agricultural products.
High-density polyethylene (HDPE plastic) is the stiffest type of PE. It is a stronger and stiffer polyethylene than LDPE or LLDPE. The HDPE for rotational moulding is commonly used to manufacture products such as storage tanks and fish tanks. and is commonly used for products such as storage tanks and fish tanks.
The use of rotational moulded polyethylene enables even the most complex shapes and designs to be moulded, which is key in custom moulding products.
Optimizing product quality - melt flow rate in rotational moulded polyethylene
The melt flow rate (MFR) of polyethylene in rotational moulding is an important property to consider when selecting the right polyethylene resin for a product. It is not linked to the density but directly related to the viscosity of the polymer melt and therefore has a significant impact on the processing and final properties of the product.
A high melt flow rate indicates that the polymer has a low viscosity and will flow easily, making it suitable for fine details in the mould and thin-walled applications. On the other hand, a low melt flow rate indicates that the polymer has a high viscosity and will not flow as easily, making it more suitable for thicker-walled applications.
MFR also has an effect on the final properties of the product. Selecting the appropriate melt flow rate of rotational moulded polyethylene is crucial as it can affect the strength, chemical resistance, and surface finish of the final product. It’s important to take into account all the properties required for the product when making this decision.


Crosslinked polyethylene in the manufacture of robust products
Crosslinked polyethylene, often abbreviated XPE, is a special version of polyethylene for rotational moulding. In a process known as crosslinking, chemical bonds are formed between the polymer chains of PE to improve its properties. This increased crosslinking not only increases the durability of the material, but also enhances its resistance to heat, chemicals, and stress. As a result, crosslinked polyethylene is often chosen for high-performance applications where its unique properties are crucial.
In the rotational moulding process, crosslinked polyethylene allows for the creation of products with increased durability and better resistance to external conditions, which is particularly important in the manufacture of large tanks and other items that must withstand harsh operating conditions. However, while crosslinked polyethylene offers excellent performance, it presents challenges in terms of recyclability. The bonds formed during the crosslinking process make it difficult for the material to melt evenly, which limits recyclability.
PE foam creates sandwich constructions
The rotomoulding process allows us to produce products with a unique construction: two outer layers of rotational moulded polyethylene (PE) filled with a PE foam core. This sandwich-like structure increases the rigidity of the product while maintaining a low weight.
This construction technique is particularly beneficial for the production of large open containers, such as fish containers. The inherent rigidity provided by the sandwich structure makes it ideal for storing and transporting heavy loads, while the lightweight nature of the material makes it easy to handle and transport. The outer PE layers and PE foam core form a unified structure – the layers cannot be separated. This consistency not only enhances the structural integrity of the product but also prevents the layers from delaminating or separating over time.
Because this multi-layer construction is made of layers of the same polyethylene for rotational moulding, the product retains its recyclability. This means that at the end of its lifecycle, it can be recycled and reused, contributing to sustainable production practices and reducing environmental impact.

Polyethylene rotational moulding - benefits and limitations
Rotational moulded polyethylene is a popular material for rotomoulding due to its strength, ductility, and resistance to corrosion and chemicals. Despite its many advantages, the material has its limitations. It has limited thermal resistance, which means that it can soften at high temperatures. In addition, polyethylene may exhibit lower mechanical strength compared to other materials, which may require additional structural reinforcement. PE is prone to creep, which means it can deform over time under loads. This can affect its dimensional stability and reduce the strength of a product under continuous load. Polyethylene is also not suitable for high-pressure applications such as pipes for gas distribution or fluid transportation, or for pressure vessels.
In the rotational moulding process, polyethylene allows for the production of large, uniform items without seams, which is crucial for the strength and aesthetics of the final product. Although PE has many advantages, it is important to be aware of its limitations and choose the right grade of polyethylene for your specific application and use – LDPE, LLDPE and HDPE in rotational moulding.
Our experts can advise you on the right material and type of rotational moulded polyethylene for your products, ensuring optimum technical performance and appearance of the final product.
your idea
to life. Start now!


